-
General Article

- Exploratory measurement of the complexity of old-building reconstruction projects: A Case study in Vietnam
- Minh Van Nguyen, Tu Thanh Nguyen, Khanh Duy Ha and Jinkook Yang
- A literature review noted the limitations of complexity measurement in old-building reconstruction projects. A three-stage complexity measurement framework was developed using a …
- A literature review noted the limitations of complexity measurement in old-building reconstruction projects. A three-stage complexity measurement framework was developed using a model based on the Fuzzy Synthesis Evaluation (FSE) method. Expert interviews and questionnaire surveys were then used to validate the framework practically in an old-building reconstruction project. The three-stage complexity measurement framework was validated to be reliable and practical. The findings revealed an overall complexity index of 4.078, indicating considerable complexity in the case project. The technological aspect of the project was identified as the most complex group, followed by organizational and environmental complexities. This study contributes significantly to the existing knowledge by presenting a conceptual model for evaluating the complexity of old building reconstruction projects. This study also emphasizes the benefits of the FSE approach, which is user-friendly and easily computable. - COLLAPSE
-
General Article

- Effect of unit layout and façade design on high-rise apartment indoor daylight conditions in tropical climate
- Najib T. Al-Ashwal, Yaik-Wah Lim, David B. Dalumo, Pau Chung Leng, Noraslinda Abdul Rahamn and Sharifah S.S. Mahdzar
- The rapid urban population growth and land scarcity in major cities have resulted in the development of high-density, high-rise apartment buildings as …
- The rapid urban population growth and land scarcity in major cities have resulted in the development of high-density, high-rise apartment buildings as a common urban housing typology. Given their density and layout efficiency, apartment living units usually rely on windows on one side to receive natural lighting despite the abundance of daylight in the tropical climate. Therefore, this paper investigates the daylight conditions in three selected high-rise apartments with different layouts and orientations in Johor Bahru, Malaysia. Field measurements were conducted using illuminance sensors with data loggers in three selected high-rise apartments for 4-5 days. The measurements were carried out in different months to capture variations in daylight conditions. The measurement results revealed that units with a room depth of less than 2.5 times window height (H) experienced high illuminance levels, particularly near the external windows. In contrast, units with a room depth of more than 2.5 H exhibited lower illumination levels, necessitating electric lighting to illuminate the deeper areas of the rooms. This study contributes to the existing literature by providing empirical field measurements of daylight conditions in high-rise apartments in a tropical climate. While previous studies have relied primarily on modelling and simulation, this research offers real-world insights into the effects of room layout, window size, and adjacent shading on daylighting performance. - COLLAPSE
-
General Article
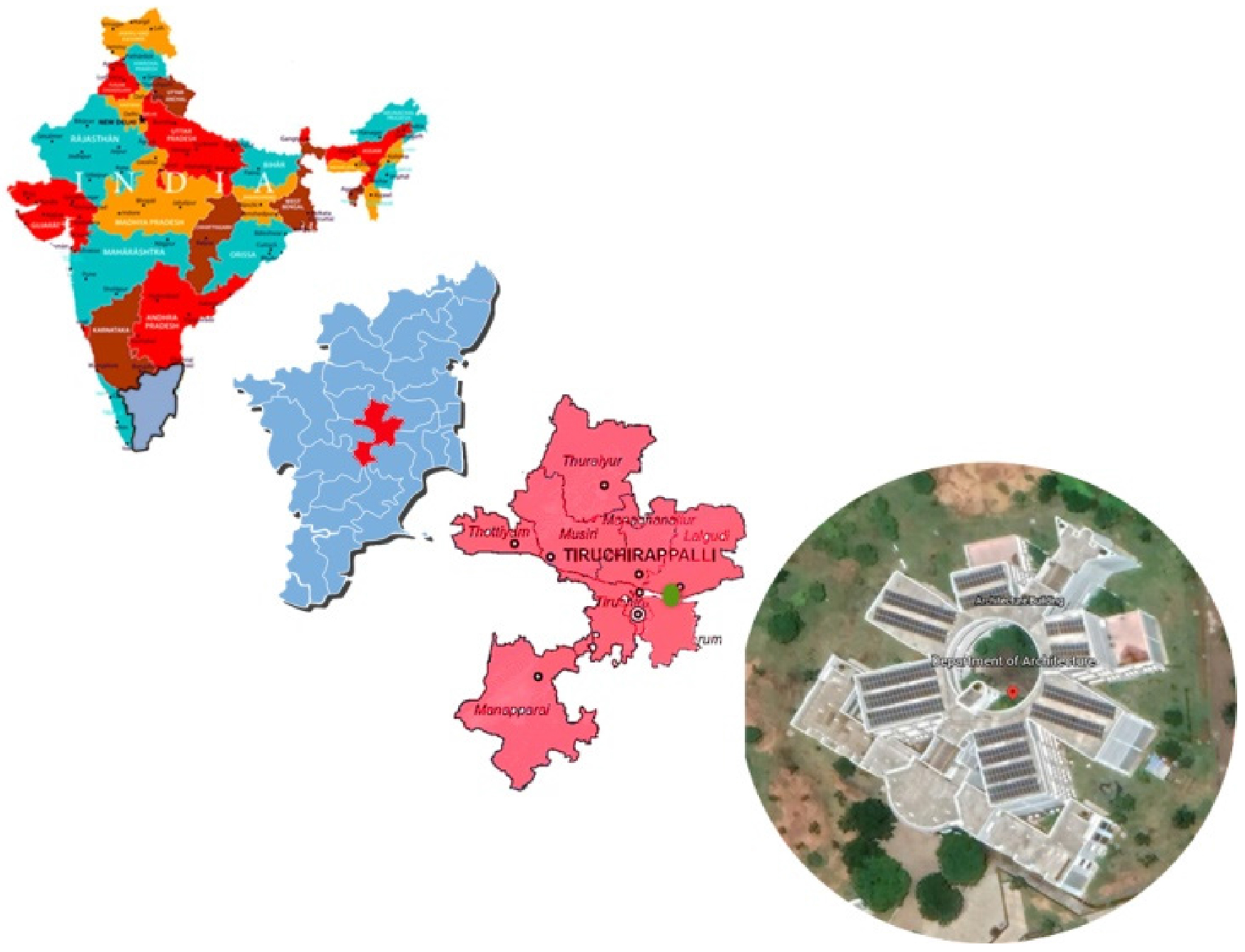
- The importance of building orientation in academic spaces: A Mathematical approach
- Shanmuggarani Ayyapan and Kannamma Dorairaj
- A mathematical model has been developed in this study to explain the variation in room/corridor temperature distribution in a preferentially oriented (-45°North) …
- A mathematical model has been developed in this study to explain the variation in room/corridor temperature distribution in a preferentially oriented (-45°North) academic complex, located in southern India. The shadow area yield, room temperature, and corridor temperature were measured over time using field experiments, and these measurements have been validated with building simulation results. Extensive solar analysis has been conducted to assess the overall air progress inside the classrooms through the window openings. Based on the experimental/simulation results, it has been observed that the eastern side of the academic space gets heated up faster than its western counterpart. The corridor/room temperature profiles obtained from the experiments and simulations are found to mimic a cubic function, with minor deviations. - COLLAPSE
-
General Article
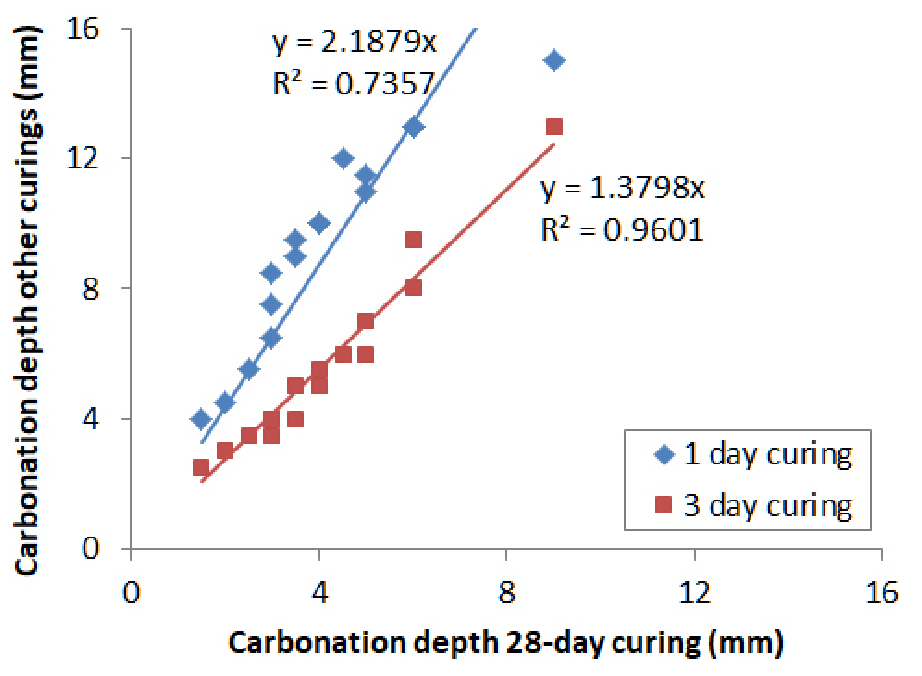
- Natural carbonation of concrete: An Initiation model for service life prediction
- Quoc Huy Vu, Gabriel Pham, Bruno Huet and Rémi Barbarulo
- A full predictive engineer model with a limited number of calibrating parameters for natural carbonation of concrete is derived, calibrated and validated. …
- A full predictive engineer model with a limited number of calibrating parameters for natural carbonation of concrete is derived, calibrated and validated. The model relies on the experimental link between natural and accelerated carbonation. The model is based on the concrete mix-design, the curing period and the climatic conditions as input parameters. The model is calibrated and validated on experimental data published in the recent scientific literature covering 1) a water to binder ratio from 0.4 to 0.8, 2) a percentage of clinker from 15 to 100%, with limestone, slag, fly-ash, pozzolan as supplementary cementitious materials, 3) climatic data characterized by an annual temperature from 10°C to 27°C, a RH from 34% to 76% and a number of rainy days per year from 9 to 90 days, 4) a curing duration from 1 day to 6 months. The accelerated carbonation rate is estimated with the mix design with reasonable number of fitting parameters. A simple relationship links natural carbonation in sheltered condition protected from rain to accelerated carbonation by considering the effect of exposure temperature and relative humidity, the impact of curing and a correction factor proving the relevance of using an accelerated test as a durability indicator as proposed in the standards. The model reproduces the carbonation with an uncertainty of a few millimeters for both early age and mature curing in controlled, sheltered and unsheltered carbonation conditions. This allows a step further towards the estimation of the whole service life of structures in real climate and curing conditions. - COLLAPSE
-
General Article

- Design of net zero energy phygital office building - A Future prospective study
- Swetha Kuna and Michael Brazley
- There is a growing concern about the rising energy crisis and climatic change. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, the increasing …
- There is a growing concern about the rising energy crisis and climatic change. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, the increasing number of office buildings hosting numerous employees significantly contributes to energy consumption. With the awareness about sustainability and advancement in green innovations, the building sector is being driven considerably towards energy-efficient design strategies and reducing the carbon footprint. The concept of a Net Zero Energy Building (NZEB), which produces as much energy as it uses over a year, has evolved from research to reality. The present study aims at a sustainable design approach with careful attention to the building site and layout, building envelope, and Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC), ultimately reaching the net-zero energy goal. The research also utilizes the strategies of a phygital office, connecting physical and digital working environments that provide a flexible and interactive experience for the employees. The expected outcome is the design of a Net Zero-Energy Phygital Office Building, paving a new path for a sustainable environment. - COLLAPSE
-
General Article

- Household metabolism and environmental impacts of household consumption on urban city –Systematic review
- Nour Abdeljawad, Imre Ferto and Imre Nagy
- Household metabolism evaluation is an important concept for urban development because it helps in resource efficiency transition. This research is intended to …
- Household metabolism evaluation is an important concept for urban development because it helps in resource efficiency transition. This research is intended to map the current household metabolism literature to discover and highlight the obstacles to household expenditures in terms of food consumption and waste produced, as well as the environmental impact of sustainable consumption in cities. The study systematically reviews the papers on household metabolism in cities from 1995 until the end of March 2021. We used the PRISMA framework for systematic literature searches in Web of Science, SCOPUS, Science Direct, and other databases. Only 71 papers were declared acceptable for review in the analysis after a thorough selection procedure, and we chose only 58 for quantitative analysis. Additionally, we conducted a bibliometric analysis of the literature to highlight countries’ efforts on household metabolism. The results revealed that most of these studies are focused on specific domains (e.g., direct and indirect energy, water, or waste production), but few studies focused specifically on household food metabolism, waste, and indirect energy as a result of food consumption. The paper concludes after analysing the literature and methodologies used for quantifying and evaluating direct and indirect environmental loads, factors of food consumption and waste resulting from households, and their potential application in sustainable development to ensure sustainable consumption and production patterns and resource efficiency. Finally, we linked the identified results from the recent findings with policies and identified areas for future research needs. - COLLAPSE
-
General Article
- Critical views on AI (Artificial Intelligence) in building design
- Choulwoong Kwon and Yonghan Ahn
- The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in architecture and building design heralds a transformative era characterized by significant enhancements in efficiency, cost …
- The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in architecture and building design heralds a transformative era characterized by significant enhancements in efficiency, cost savings, and data-driven decision-making. However, this technological shift presents critical challenges that threaten to undermine the core principles of architectural practice. This paper critically examines the impact of AI on the architectural profession, focusing on three major concerns: the deprivation of human thinking, the loss of personal character in design, and the reduction of humans to simplistic beings. First, the paper explores how AI's reliance on pre-existing data and algorithms may stifle innovation, turning architects into mere operators who lack the deep understanding and creative problem-solving skills essential to their craft. Second, it addresses the potential loss of personal expression and artistic vision in architecture, as AI-generated designs tend to be homogenized and devoid of the unique perspectives that individual architects bring to their work. Lastly, the paper delves into the broader implications of overreliance on AI, warning that it could lead to a reduction in human cognitive abilities, reducing architects to simplistic beings driven by technology rather than creativity and intellect. The paper concludes by advocating for a balanced approach that leverages AI as a tool to enhance human creativity and decision-making without replacing it. By maintaining a human-centric approach to design, architects can ensure that AI enriches the built environment rather than diminishing the cultural and intellectual richness that defines human civilization. This balanced integration of AI in building design is crucial for preserving the essence of human intelligence and artistic expression in architecture. - COLLAPSE
-
General Article
- Study on elderly living facilities evacuation based on PATHFINDER simulation
- Lianlian Quan and Chiwon Ahn
- With the continuous deepening of the aging process in society, the safety issues of elderly living facilities, as important living places for …
- With the continuous deepening of the aging process in society, the safety issues of elderly living facilities, as important living places for the elderly, are increasingly receiving widespread attention. In this paper, we analyze the relationship between floor plan and elderly evacuation, and simulate the evacuation situation of elderly people under different plan layouts using PATHFINDER simulation software. The simulation results, through data analysis, demonstrate a certain correlation between plan layout and evacuation time. The research results of this paper are as follows: the larger the total building area and the more floors, the longer the total evacuation time is required. When The evacuation route in the building has a folded corner, the density will increase, leading to queuing and a series of problems such as falling. In small-sized elderly living facilities, the evacuation situation is almost the same when the distance between the evacuation staircase and the exit to outside is far, and the evacuation doors are adjacent to each other. These conclusions provide some suggestions for designers from the perspective of safe evacuation. - COLLAPSE
-
General Article

- An assessment of work-related stress under sustainable urban areas and causes among working women performance
- Deepthi M, Mamta Rana, H Ganesan, Sukhpreet Singh, Deepak Sharma, Ramesh Chand, JV Muruga Lal Jeyan and Abhinav Kumar
- Workplace stress is a troubling health issue that should be avoided by taking the necessary precautions because it could have major socioeconomic …
- Workplace stress is a troubling health issue that should be avoided by taking the necessary precautions because it could have major socioeconomic repercussions in sustainable urban areas. In Ludhiana’s industrial sector, workplace stress significantly affects employees’ health and urban sustainability. Rotating shift workers face a 2-fold risk of stress (Adjusted odds ratio=2.37, 95% CI=1.41-3.41), exacerbated by inadequate social support (Adjusted odds ratio=3.71, 95% CI=2.92-5.12) and moderate social support (Adjusted odds ratio=3.11, 95% CI=1.81-4.92). Salary dissatisfaction also increases stress among women (Adjusted odds ratio=2.57, 95% CI=1.32-2.97). Proactive stress management is essential to maintain productivity and prevent workforce turnover. - COLLAPSE
-
General Article
- Future archaeology in the digital age
- Kidong Bae
- Perception, consciousness and behaviour in digital cyber-space has been increased along with those in natural space in modern days. Electronic and magnetic …
- Perception, consciousness and behaviour in digital cyber-space has been increased along with those in natural space in modern days. Electronic and magnetic residue as results from behaviour in digital space should be pursued by modern archaeology as other objects in conventional archaeology; stone, pottery, metals etc. While digital archaeology for archiving archaeological contents digitally and cyber-archaeology attempting digital reconstruction of archaeological sites on basis of current knowledge, archaeology of digital age should do researches of modern behaviour in digital space which is different from those in natural space, in particular born-digital behaviour that will be increased dramatically in future as seen in the case of NFT and blockchain. As rapid evolution of digital technology and culture may leave numerous digital sites in cyber-space as the case of the original ‘cy-world’, archaeology of cyber-space constructed by digital technology should be established and carried out immediately before important evidence of human behavior in cyber space will be lost, in collaboration of other fields of anthropology and electronic science, as an extended version of ‘multi-anthropology’, whatever the title of field would be. - COLLAPSE
Journal Informaiton
 International Journal of Sustainable Building Technology and Urban Development
International Journal of Sustainable Building Technology and Urban Development
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 International Journal of Sustainable Building Technology and Urban Development
International Journal of Sustainable Building Technology and Urban Development













